Buy Maker Dai
Maker Dai
DAI
Overview
What is Maker Dai?
What is Maker DAI? Want to buy DAI on CoinJar? Here’s what you need to know.
Understanding MakerDAO and the DAI Stablecoin
MakerDAO is a decentralized autonomous organisation (DAO) built on the Ethereum blockchain. Its mission is to create a stable and decentralized digital currency. Let’s dive into the details of what Maker DAI is and how you can acquire it.
What is DAI: The simple explanation
Here’s a simple way to describe how it works. Imagine you have a coin called “DAI.” It’s like a regular coin, but it always tries to stay worth the same as one U.S. dollar.
So how does it stay stable? It is created using something called a “smart contract” on the Ethereum blockchain. Think of this smart contract as a set of rules that govern how the crypto works.
Say you have some Ethereum (ETH). You can use it as a kind of security deposit to create Dai. This is done through a platform called the Maker Protocol.
Think of it like this: You put your ETH in a digital vault called a “Collateralized Debt Position (CDP)”. It's like putting your ETH in a safe. Then, the Maker Protocol gives you Dai in return, based on how much ETH you put in.
Now, here's the catch: Because the value of cryptocurrencies can change a lot, you have to put in more ETH than the value of the Dai you want to get. This is called over-collateralization.
For example, if you want $100 worth of Dai, you might need to put in $200 worth of ETH. This is to make sure that even if the value of ETH goes down, there's still enough value to cover the Dai.
When you want to get your ETH back, you have to return the Dai you borrowed, plus a small fee for using the Maker Protocol. It's like paying rent for using the vault.
So, in simple terms, Dai is digital money you can get by trading it for Ethereum, or by using Ethereum as a deposit in a special digital vault called a CDP.
What stability means for users
DAI ideally offers stability (but nothing is guaranteed in stablecoin world!). This is good for things like online shopping (mostly with merchants accepting funds via payment companies that enable crypto payments). You can theoretically use it to buy things online, just like using dollars.
Regular cryptocurrencies (like Bitcoin) can swing up and down a lot in price. DAI aims to stay steady in price.
When you send DAI to someone in another country, they should get the same value without worrying about exchange rates.
Say your cousin in America needs some cash. Instead of dealing with exchange rates and bank fees, you send them DAI instead. This is without all the bank fees and then the banks converting currency in their favour.
Because the price theoretically stays stable, people use it in decentralised finance (DeFi) apps. These apps let you lend, borrow, and earn interest.
Other uses
It has other uses. Imagine you’re a crypto trader. When other coins swing wildly, you can switch your existing crypto into DAI to keep stability.
You can lend your DAI on platforms like Compound or Aave. Your DAI earns interest, and you don’t lose sleep over price fluctuations.
What is DAI? A more technical explanation
It is a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar. Unlike other cryptocurrencies, its value remains relatively stable, making it suitable for everyday transactions.
It is created through a system of collateralised debt positions (CDPs). Users lock up crypto assets (such as Ethereum) as collateral to generate DAI.
The collateralization ratio determines how much of it can be minted against the locked assets.
If the value of the collateral drops, users may need to add more assets or repay part of their debt.
Outstanding debt refers to the total amount of DAI in circulation.
MakerDAO components
Smart contracts
MakerDAO relies on smart contracts to manage the creation and redemption of DAI. These contracts ensure transparency and security.
MKR tokens
MKR is the governance token of MakerDAO. MKR holders participate in decision-making processes, including voting on stability fees and other protocol changes.
Stability fee
When users create DAI, they pay a stability fee. This fee compensates MKR holders and helps maintain the stability of the system.
DAI Savings Rate (DSR)
The DSR allows users to earn interest by holding the crypto in a savings account within the MakerDAO ecosystem.
What risks should I be aware of?
DAI is backed by collateral who can themselves be volatile, such as Ethereum (ETH). If the value of the collateral drops significantly, it could trigger automatic liquidation of the collateral and cause the value of DAI to fluctuate.
It uses algorithmic smart contracts to maintain price stability and to ensure that the tokens are always kept fully collateralized. Users should be aware that other tokens which have used algorithmic smart contracts to maintain their value, such as Terra (LUNA) have failed, leading to total loss of value.







Cash, credit or crypto?
Buy Maker Dai instantly using Visa or Mastercard. Get cash in your account fast with bank transfer, Faster Payments, PayID or Osko. Convert crypto-to-crypto with a single click.How to buy Maker Dai with CoinJar
Start your cryptocurrency portfolio with CoinJar by following these simple steps.Featured In

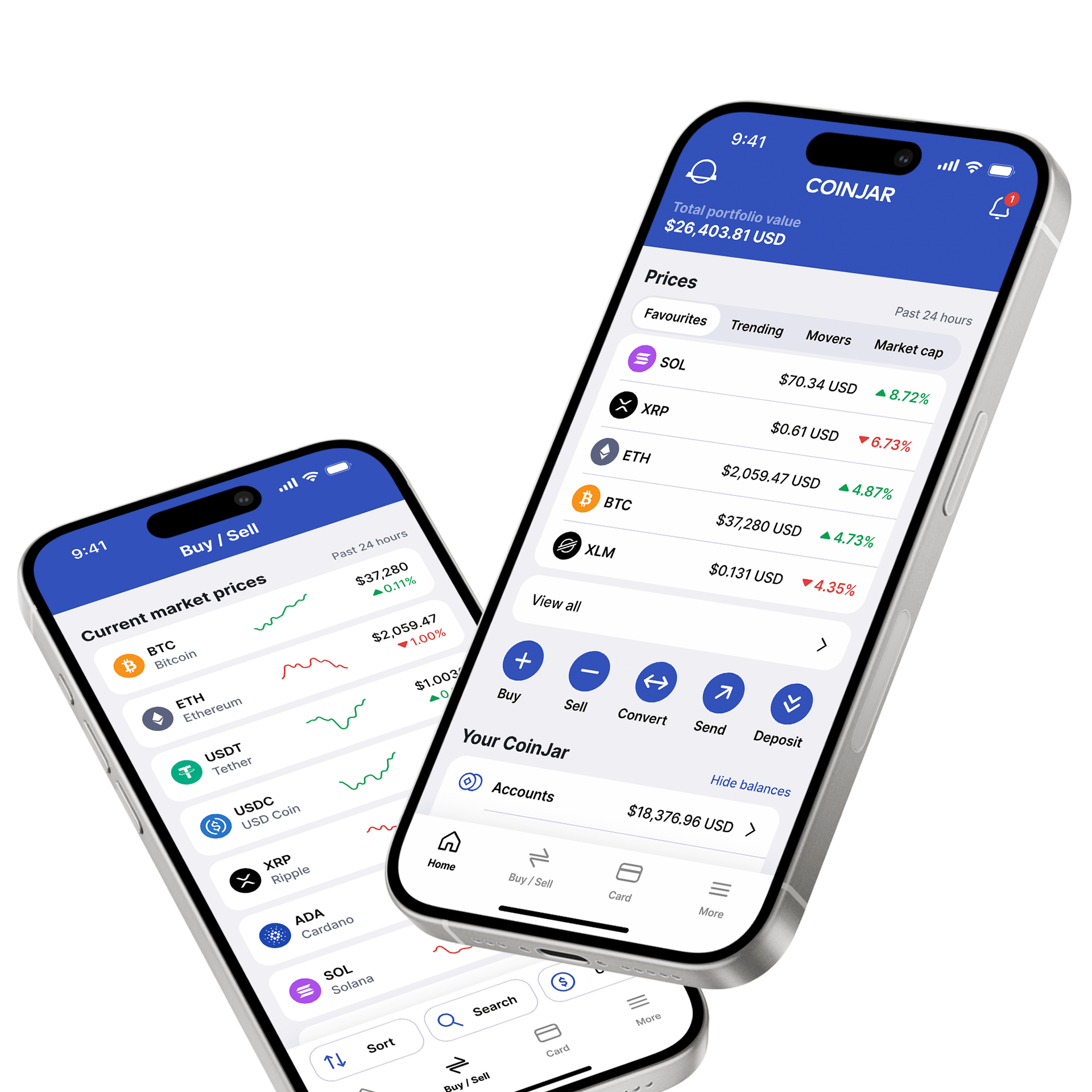
CoinJar App
All-in-one crypto walletCoinJar App
All-in-one crypto wallet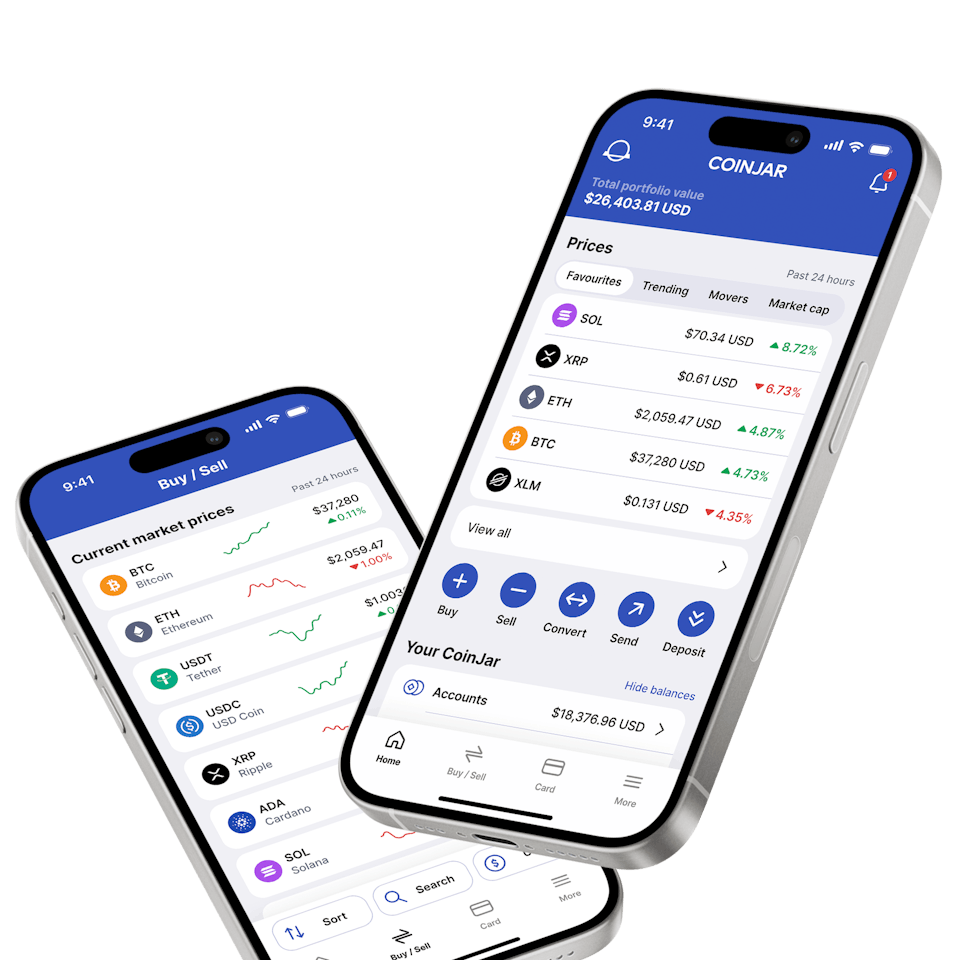
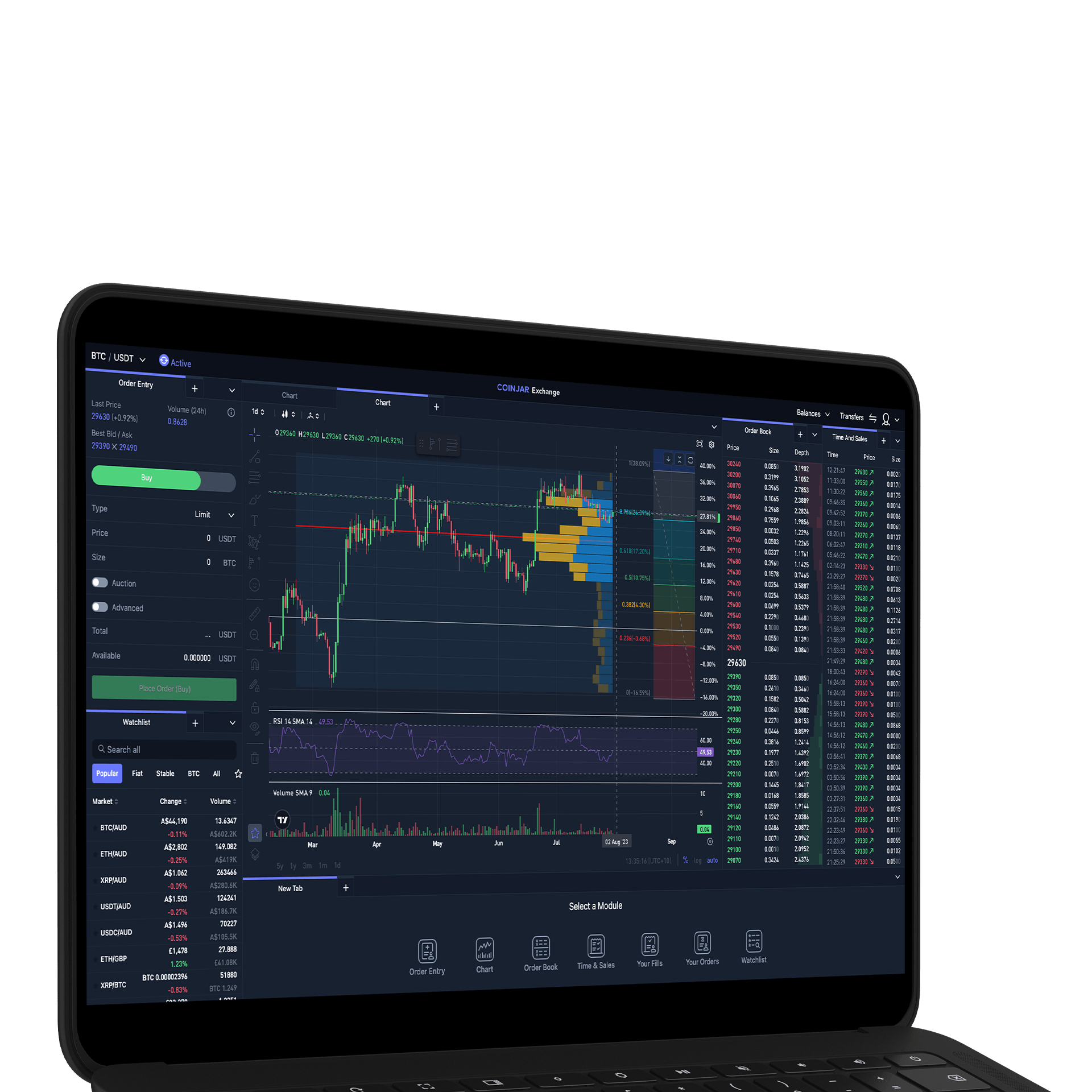
CoinJar Exchange
TRADE FOR AS LOW AS 0%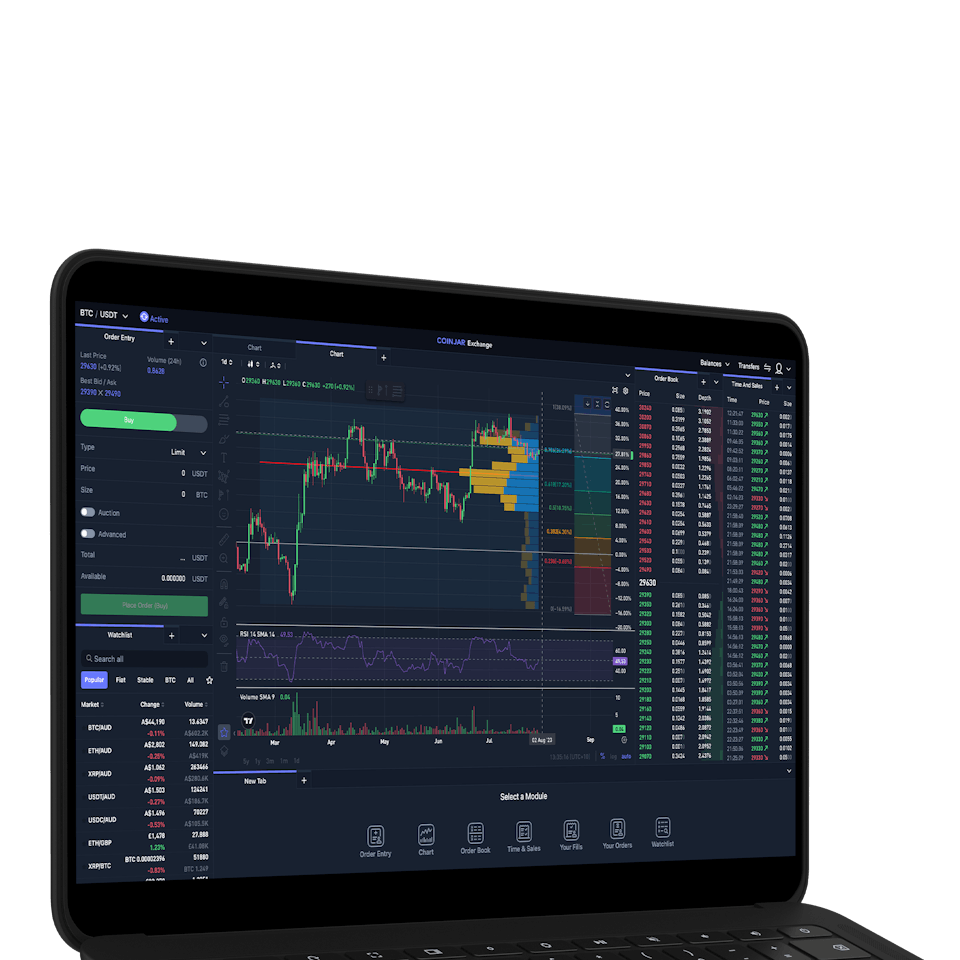
CoinJar Exchange
TRADE FOR AS LOW AS 0%CoinJar’s digital currency exchange services are operated by CoinJar Australia Pty Ltd ACN 648 570 807, a registered digital currency exchange provider with AUSTRAC.
CoinJar Card is a prepaid Mastercard issued by EML Payment Solutions Limited ABN 30 131 436 532 AFSL 404131 pursuant to license by Mastercard. CoinJar Australia Pty Ltd is an authorised representative of EML Payment Solutions Limited (AR No 1290193). We recommend you consider the Product Disclosure Statement and Target Market Determination before making any decision to acquire the product. Mastercard and the circles design are registered trademarks of Mastercard International Incorporated.
Google Pay is a trademark of Google LLC. Apple Pay is a trademark of Apple Inc.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



