Buy Universal Market Access
Universal Market Access
UMA
What is Universal Market Access?
UMA, short for Universal Market Access, is an Ethereum-based protocol that serves as an optimistic oracle. But what does that mean?
What is an oracle?
Say you are at work, and you need to know the current weather outside. You can’t step out to check it yourself, so you ask someone else (an oracle) to tell you. In the blockchain world, oracles provide real-world data to smart contracts. They bridge the gap between the digital and physical worlds.
What is an optimistic oracle?
UMA is like a “human-powered truth machine.” It verifies real-world data and brings it onto the blockchain. If there are no disputes around the data, it’s assumed to be accurate. So, UMA’s oracle system allows for various types of data to be securely integrated on-chain.
What are some interesting projects using the UMA protocol?
There are some great projects that use UMA.
Why do people buy UMA?
Decentralised Finance (DeFi)
UMA is part of the DeFi movement. DeFi aims to create financial services without relying on traditional banks or intermediaries. The UMA protocol is enables users to create decentralised financial contracts and synthetic assets.
The UMA token is also used for governance of the UMA protocol, allowing holders to vote on proposals and changes. It also incentivises participation in the network's Data Verification Mechanism, which ensures accurate price data for synthetic assets created on the platform.
Creating synthetic tokens
The UMA protocol allows anyone to create synthetic tokens tied to real-world assets (like stocks, commodities, or currencies). These synthetic tokens mirror the value of the underlying asset without directly owning it. For example, you can create a synthetic token representing Tesla stock without actually buying Tesla shares.
Governance and voting
UMA token holders have a say in the protocol’s governance. They can vote on decisions like upgrades, new synthetic assets, and dispute resolutions. When a vote happens, the total token supply increases slightly, rewarding those who participate.
How does UMA work?
Request
A smart contract requests data from UMA’s oracle. This data could be anything — stock prices, weather, election results, etc.
Propose
Someone proposes a data point. They post a bond and offer the data. If there’s no dispute during the specified period, the data is assumed true, and the proposer gets their bond back.
Dispute
If someone disagrees with the data, they can dispute it. UMA token holders resolve the dispute through voting. If the disputer is right, they get a reward; if wrong, they lose their bond.
Conclusion: Why buy UMA
UMA’s technology aims to make global markets fair, accessible, secure, and decentralised. It’s a fascinating project that combines blockchain, finance, and community governance. So, next time you hear about UMA, remember it’s not just a crypto token — it’s a bridge between the digital and real worlds.







Cash, credit or crypto?
Buy Universal Market Access instantly using Visa or Mastercard. Get cash in your account fast with bank transfer, PayID or Osko. Convert crypto-to-crypto with a single click.How to buy Universal Market Access with CoinJar
Start your portfolio with Australia's longest running crypto exchange with these simple steps.Featured In


CoinJar Card
CRYPTO SPENDING POWERED BY MASTERCARD®
CoinJar Card
CRYPTO SPENDING POWERED BY MASTERCARD®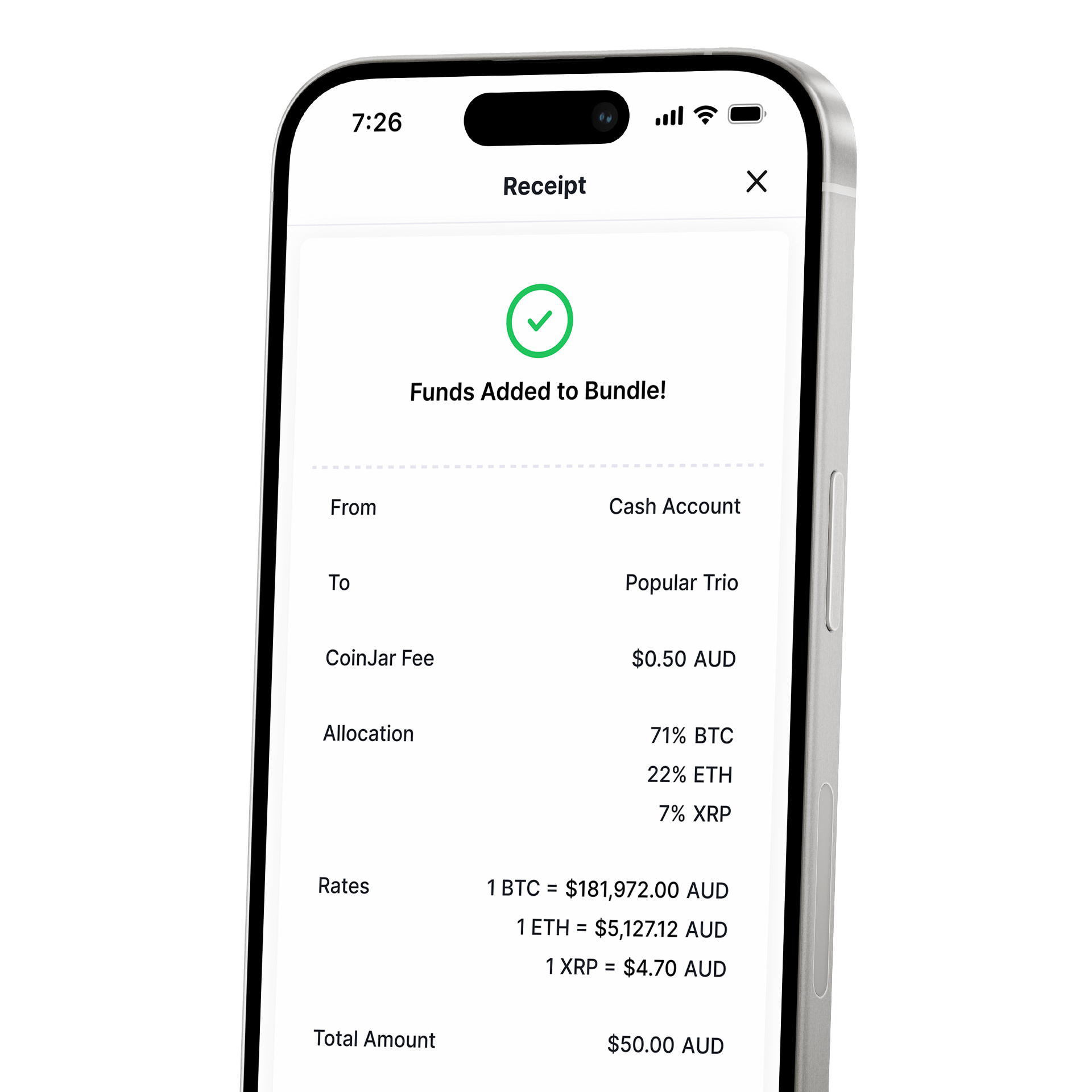
CoinJar DCA & Bundles
AUTOMATE & DIVERSIFY YOUR PORTFOLIOCoinJar DCA & Bundles
AUTOMATE & DIVERSIFY YOUR PORTFOLIO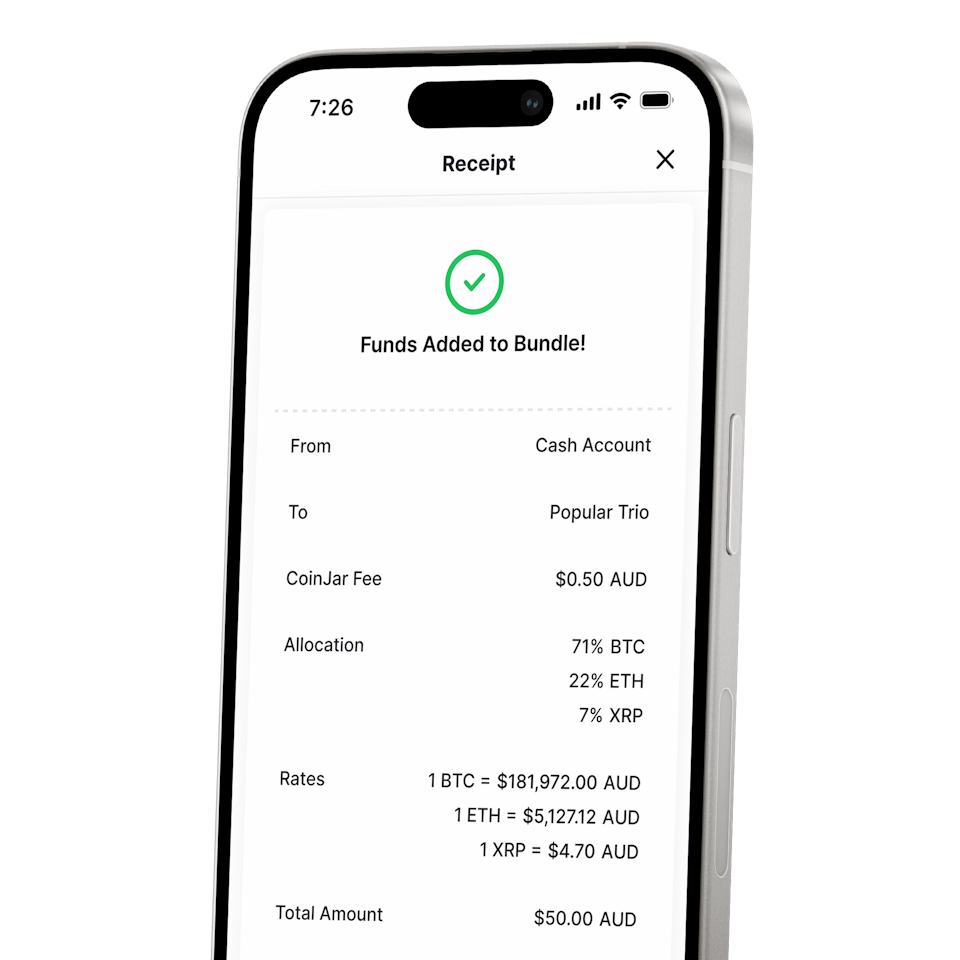
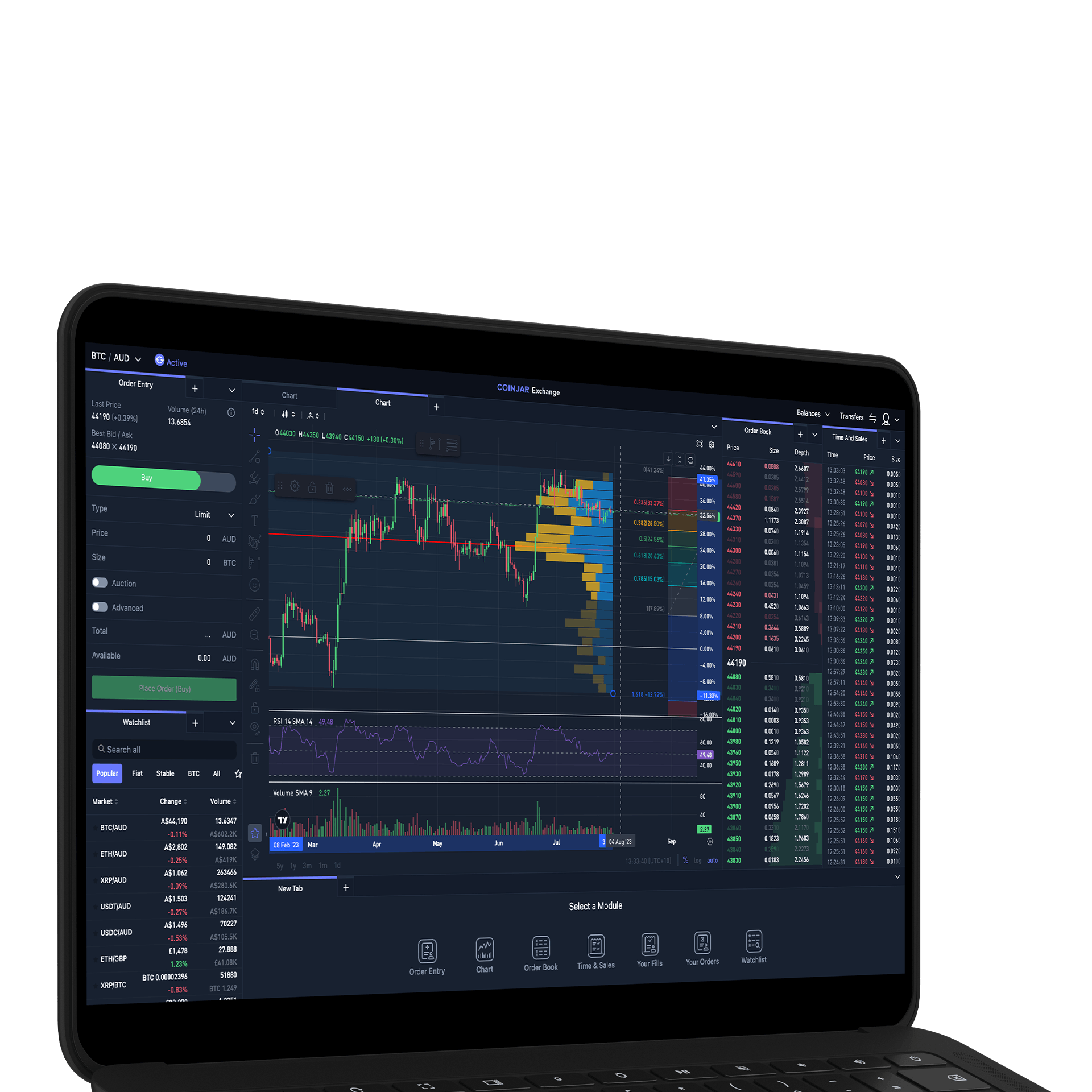
CoinJar Exchange
TRADE FOR AS LOW AS 0%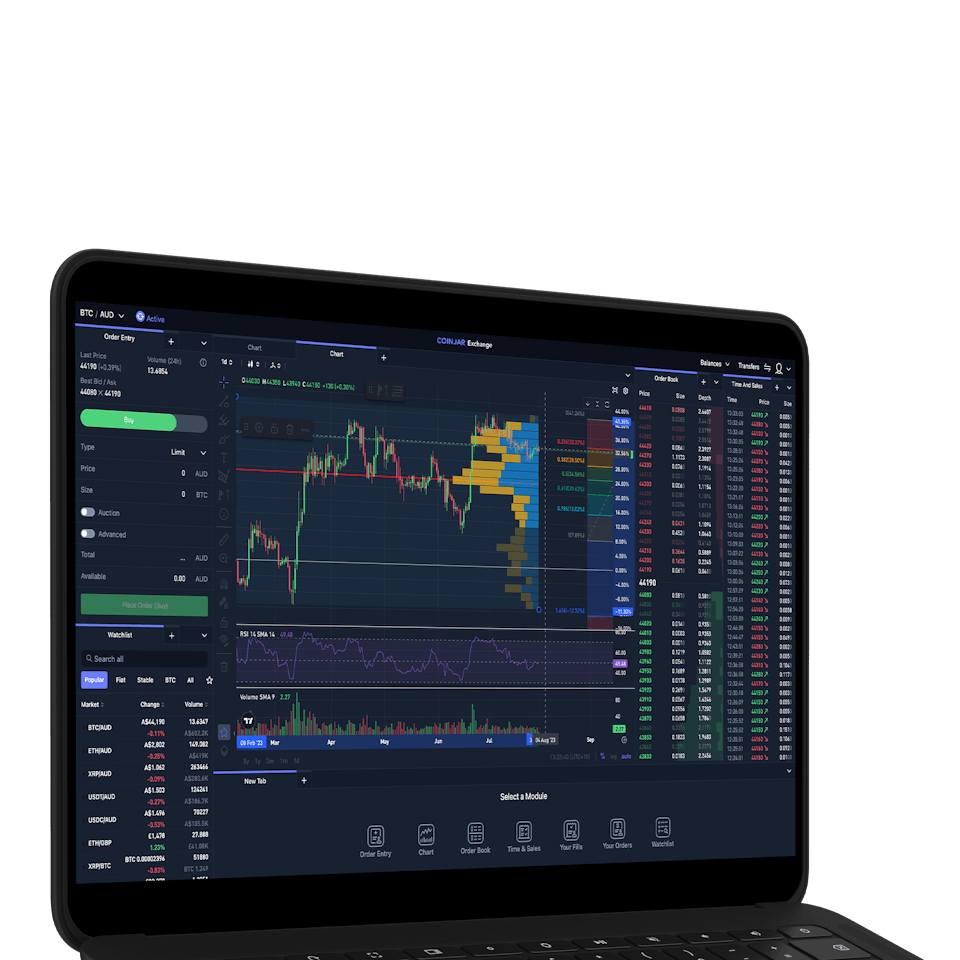
CoinJar Exchange
TRADE FOR AS LOW AS 0%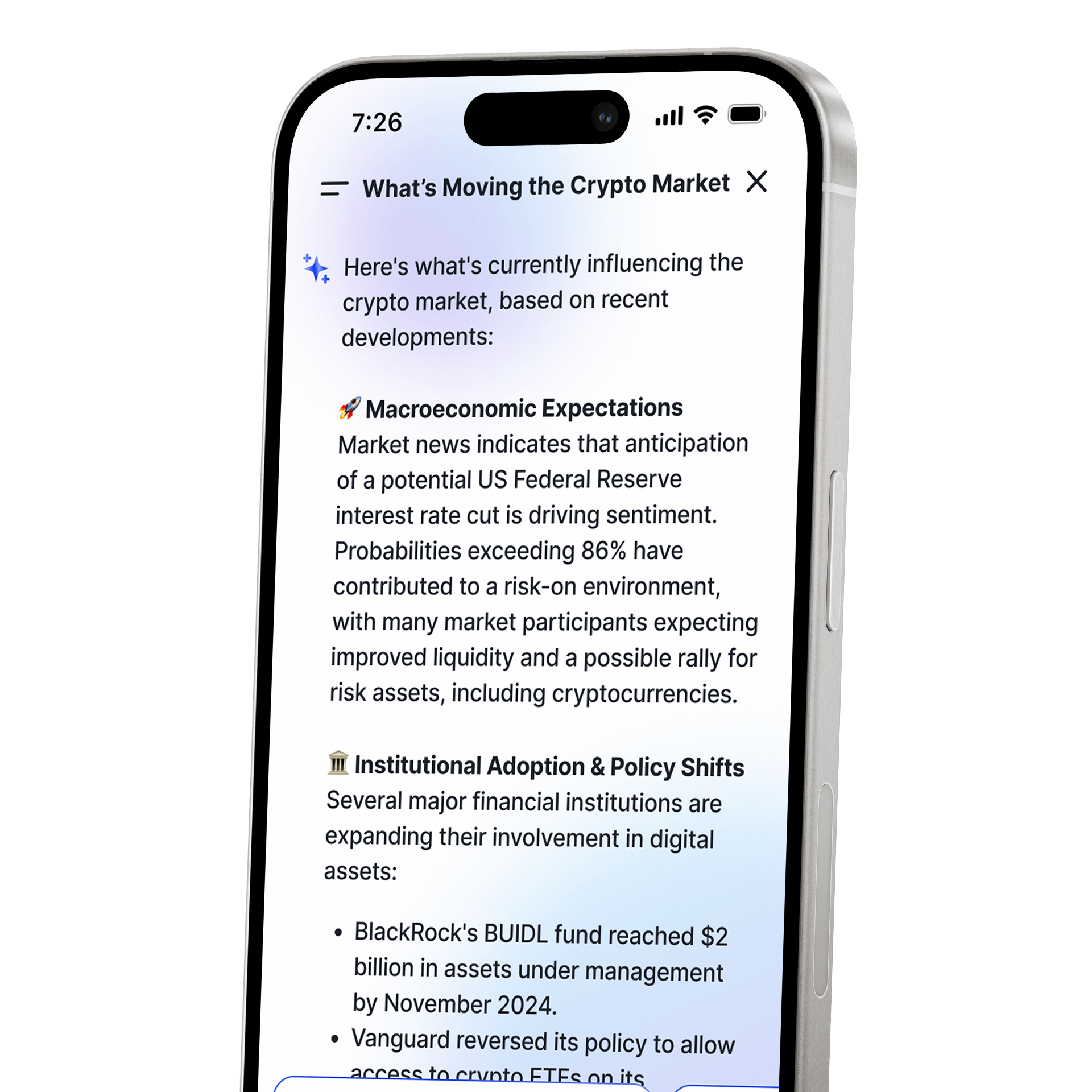
CoinJar AI
A portfolio and market assistant built into CoinJarCoinJar AI
A portfolio and market assistant built into CoinJar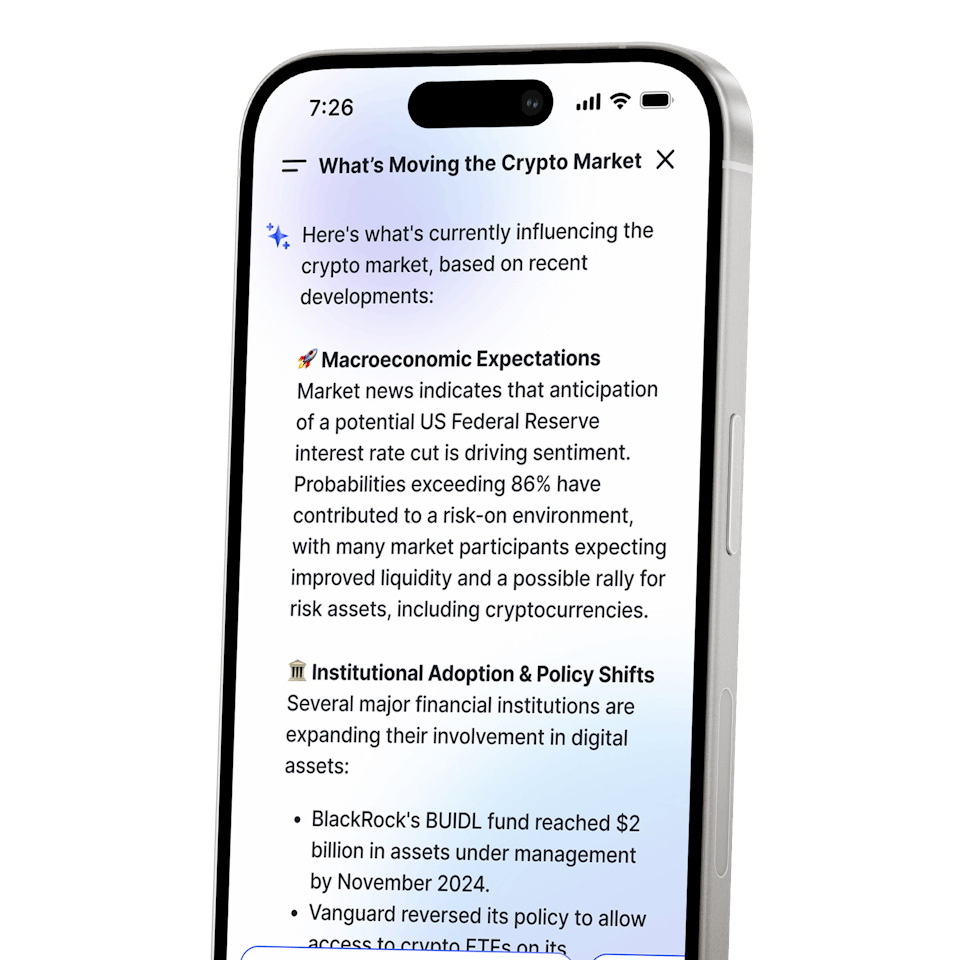
Your information is handled in accordance with CoinJar’s Collection Statement.
CoinJar’s digital currency exchange services are operated by CoinJar Australia Pty Ltd ACN 648 570 807, a registered digital currency exchange provider with AUSTRAC.
CoinJar Card is a prepaid Mastercard issued by EML Payment Solutions Limited ABN 30 131 436 532 AFSL 404131 pursuant to license by Mastercard. CoinJar Australia Pty Ltd is an authorised representative of EML Payment Solutions Limited (AR No 1290193). We recommend you consider the Product Disclosure Statement and Target Market Determination before making any decision to acquire the product. Mastercard and the circles design are registered trademarks of Mastercard International Incorporated.
Google Pay is a trademark of Google LLC. Apple Pay is a trademark of Apple Inc.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.










