Buy Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic
ETC
How to buy Ethereum Classic with CoinJar
Start your cryptocurrency portfolio with CoinJar by following these simple steps.What is Ethereum Classic?
What Is Ethereum Classic (ETC)? It is a smart contract network, where developers build and run apps (called dApps, which are apps built on the blockchain rather than on the internet). The native token of this network is ETC.
Let’s break it down.
Understanding Ethereum Classic (ETC)
The origins: Ethereum Classic’s birth
Ethereum Classic was born in 2016 as a result of a significant event in the crypto world. To understand it, we need to rewind a bit.
The DAO hack
Imagine a digital organization called The DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organisation).
It was like a venture capital fund run by code on the Ethereum blockchain. People invested their money in The DAO, hoping for great returns. But then, disaster struck! A hacker exploited a flaw in The DAO’s smart contract and drained a massive amount of Ether (ETH).
The great divide
The Ethereum community faced a dilemma. Should they reverse the hack and return the stolen funds (like hitting the “undo” button)? Or should they stick to the principle that “Code is Law,” meaning that once a smart contract executes, its outcome is final?
The split
The community split into two camps: Majority Opinion and the Rebels.
Majority Opinion
Most people chose to reverse the hack, creating a new version of Ethereum (which we now know as Ethereum or ETH).
The Rebels
A smaller group believed in the original Ethereum vision. They stood by the unaltered history and the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. This group became Ethereum Classic (ETC).
What makes Ethereum Classic unique?
Code Is Law
ETC sticks to the idea that smart contracts are like legal contracts. Once they execute, there’s no turning back. If you invest in a flawed project, you bear the consequences.
Decentralized governance
ETC’s smart contracts operate without intermediaries. No lawyers, no judges — just code. If conditions are met, the contract self-executes. If not, penalties apply.
Blockchain twins
Think of Ethereum as the older twin and Ethereum Classic as the younger one. They share DNA (the same codebase) but have different personalities. ETC retains the original Ethereum blockchain, while ETH has moved to Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
Smart contracts
What Are Smart Contracts? Imagine if contracts could execute themselves. They automatically enforce agreements when specific conditions are met.
Here are some everyday examples. Take real estate for example.
If the buyer pays the deposit by a certain date, the contract proceeds.
No lawyers are needed, the code does the job.
Smart contracts live on a distributed ledger (a fancy term for a shared database). No central authority controls them. They’re tamper-proof and transparent.
Conclusion: Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic is like the rebel sibling. It clings to the original Ethereum principles, even when the majority went a different way. So, next time you hear about ETC, remember, it’s the blockchain that believes in “Code is Law.”


Bank transfer (ACH and wire), or crypto?
Buy Ethereum Classic instantly with your bank account via ACH or deposit with wire transfer. Easily buy with ACH, wire cash to your account, or swap one cryptocurrency for another in a single click.Featured In

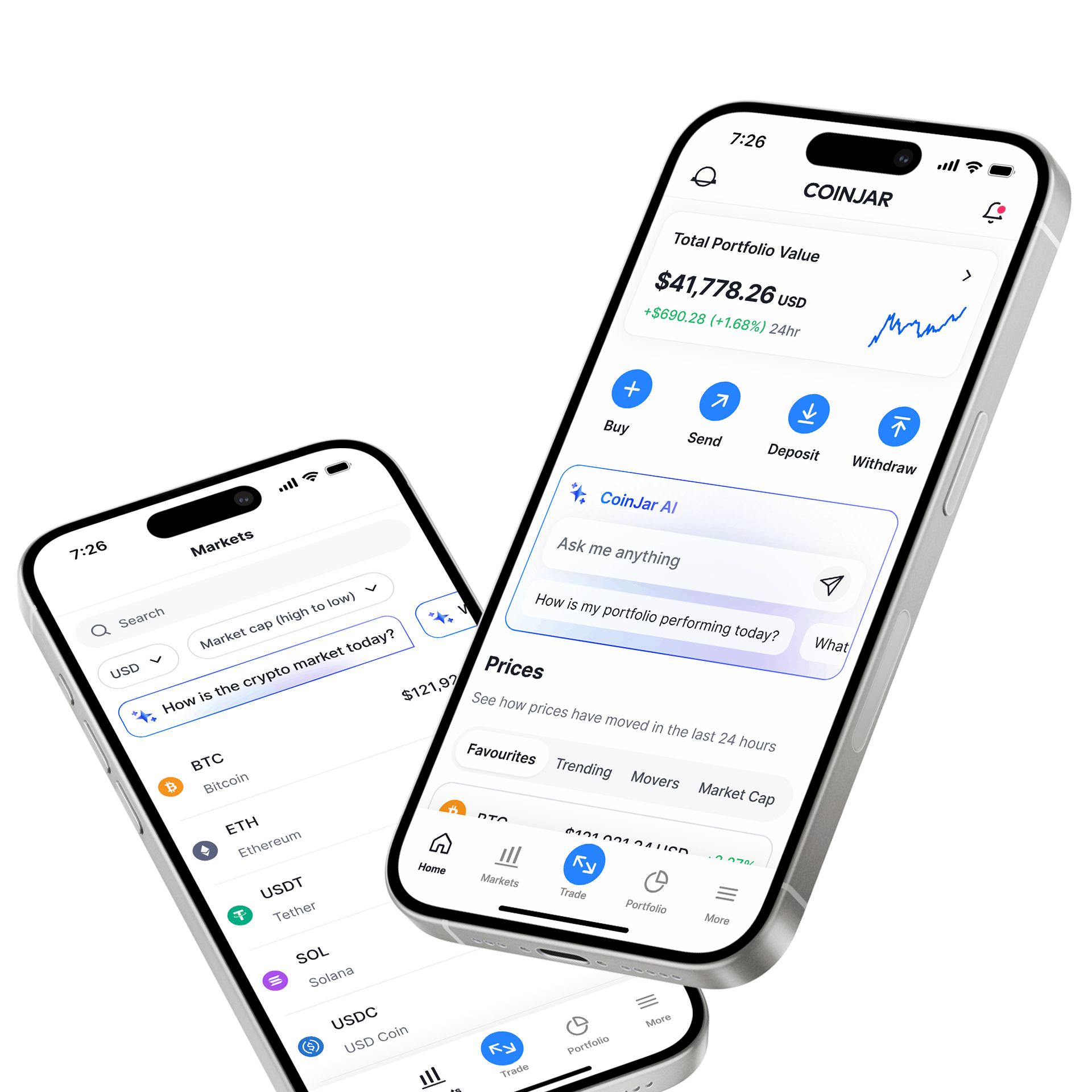
CoinJar App
All-in-one crypto walletCoinJar App
All-in-one crypto wallet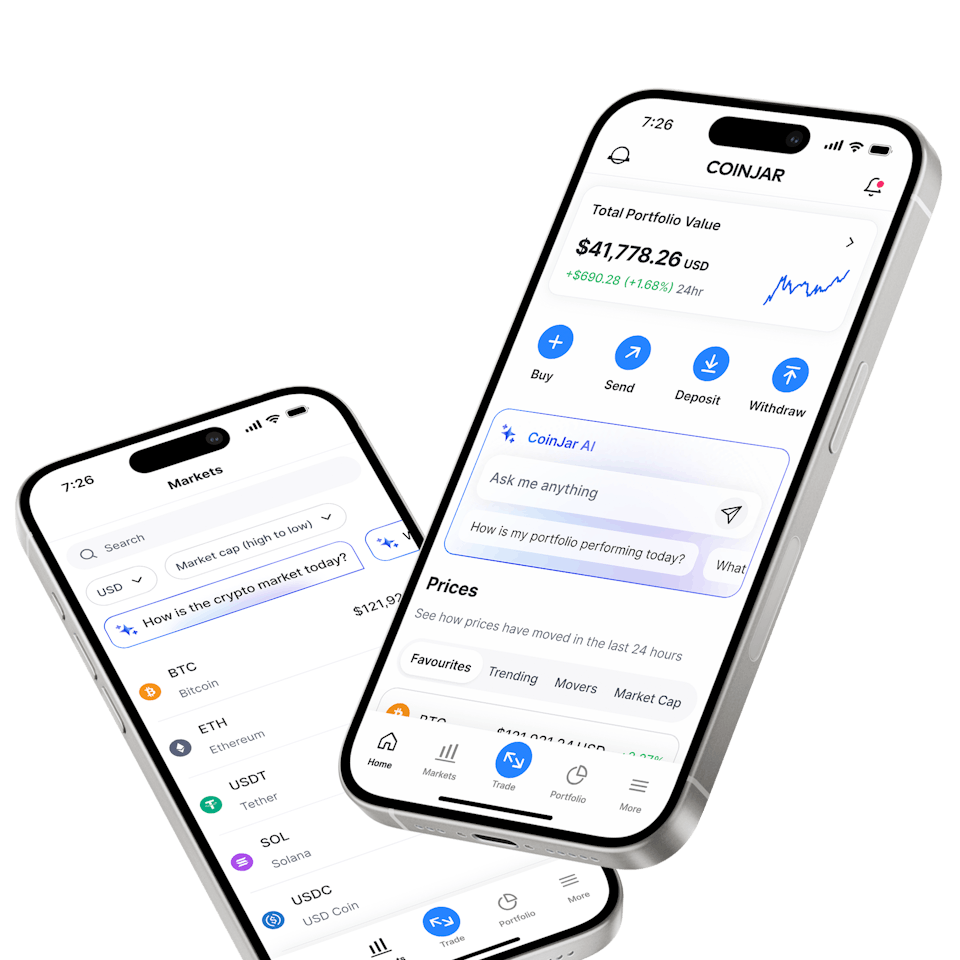
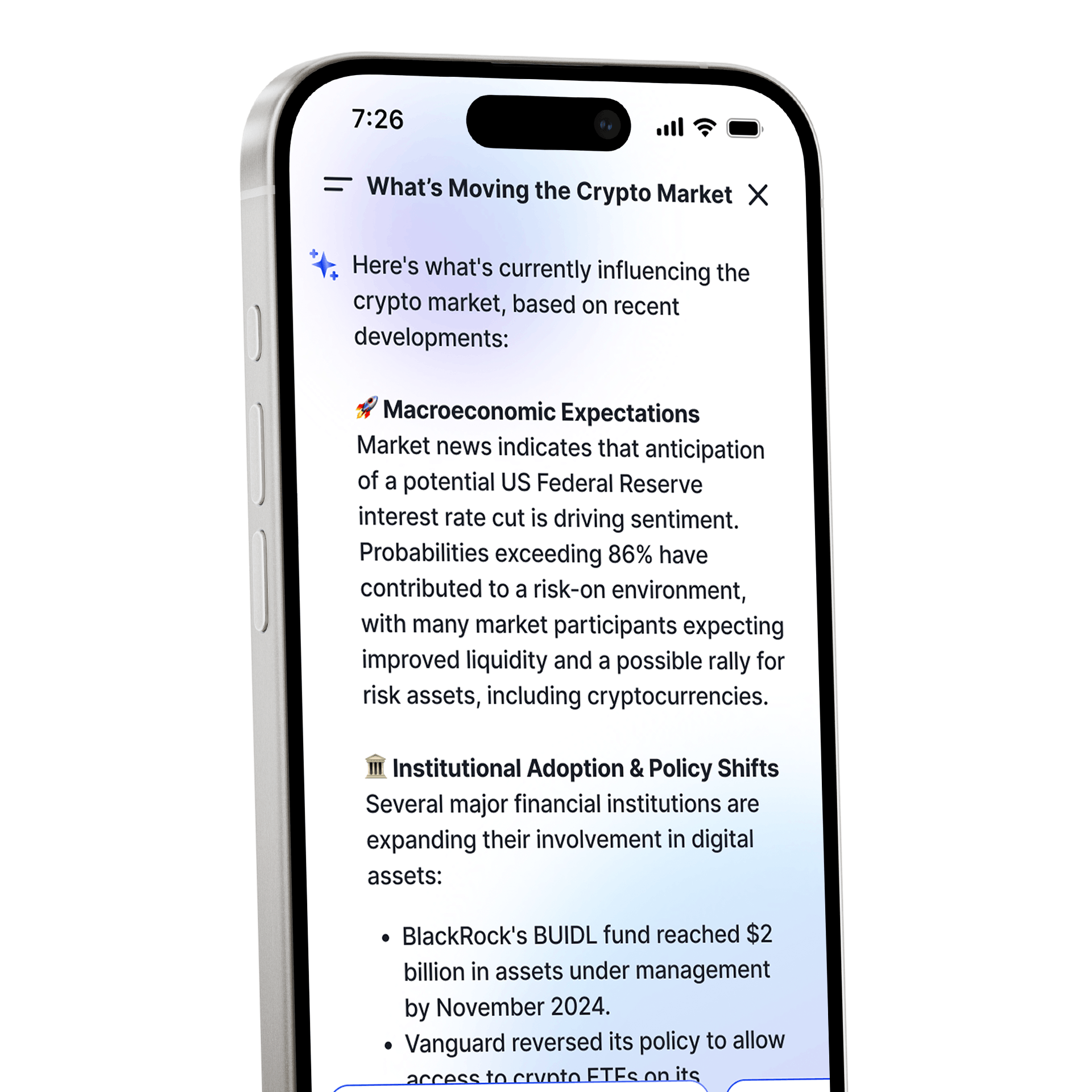
CoinJar AI
A portfolio and market assistant built into CoinJar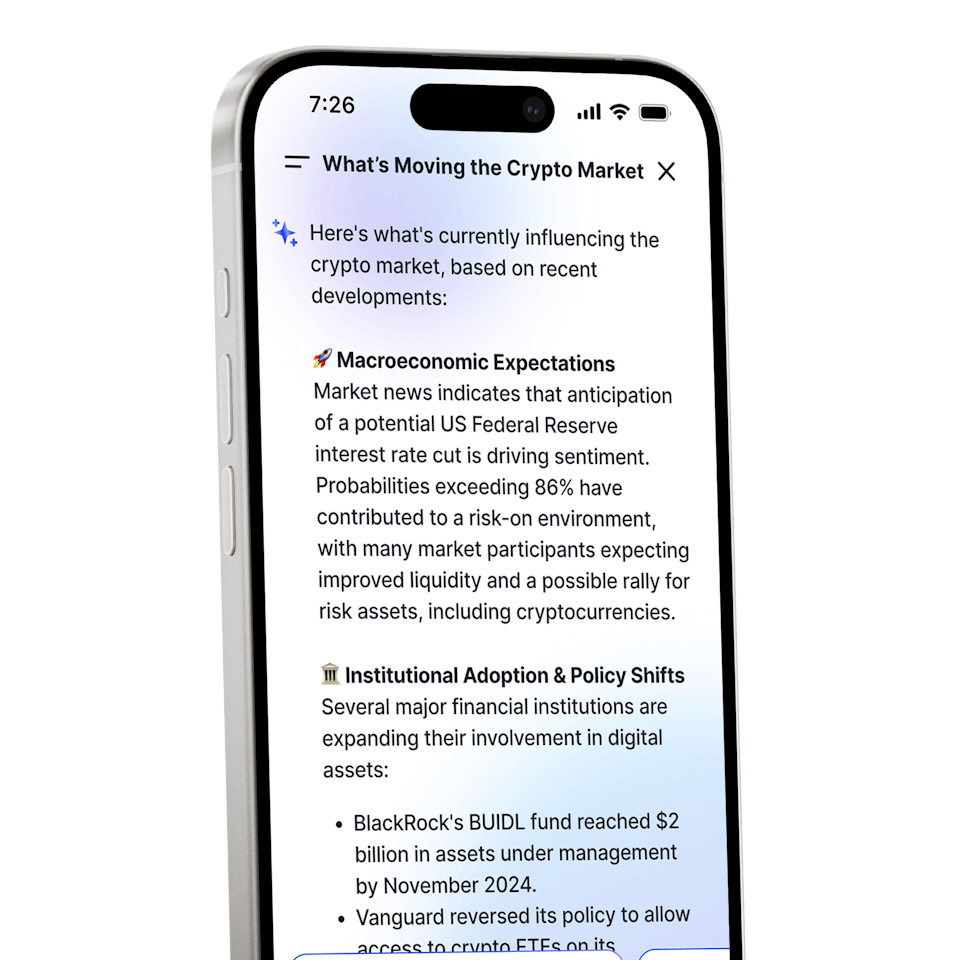
CoinJar AI
A portfolio and market assistant built into CoinJarBuying, selling, and holding cryptocurrencies is subject to high market risk. The volatile and unpredictable nature of the price of cryptocurrencies may result in a significant loss. CoinJar, inc. is not responsible for any loss that you may incur from price fluctuations when you buy, sell, or hold cryptocurrencies. CoinJar, Inc. does not provide any investment, tax or legal advice; before making the decision to buy, sell or hold any cryptocurrencies, you should conduct your own due diligence and consult your financial, tax and/or legal advisor.
It is your responsibility to determine whether any investment, investment strategy or related transaction is appropriate for you according to your personal investment objectives, financial circumstances, and risk tolerance. Enter into a transaction only if you fully understand its nature, the contractual relationship into which you are entering, all relevant terms and conditions, and the nature and extent of your exposure to loss. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results. Geographic restrictions may apply. CoinJar does not endorse the content of, and cannot guarantee or verify the safety of any third party websites. Visit these websites at your own risk.
Your information is handled in accordance with CoinJar’s Privacy Policy.
Copyright © 2025 CoinJar, Inc. All rights reserved.
CoinJar, Inc. is a registered Money Services Business with FinCEN and licensed as a money transmitter, NMLS #2492913. For a list of states in which CoinJar, Inc. is licensed or authorized to operate, please visit here. In certain other states, money transmission services are provided by Cross River Bank, Member FDIC.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.